Chocolate Production: Harvesting and Cracking of Cocoa Pods
13 February 2025
The Maturity of Cocoa Pods: A Key Factor in Bean Quality
Cocoa, a valuable product cultivated in tropical countries, begins its life as small white flowers that appear on the trunks of cacao trees. These fertilized flowers give rise to cocoa pods, which, depending on the climatic conditions and type of cacao tree, will take between five and seven months to reach physiological maturity. The color of the pod’s shell changes as it ripens. For instance, cocoa pods that begin as green typically turn yellow when they mature.
Harvesting at the wrong time can compromise the quality of the beans. If the pods are harvested too early, the beans may not have fully matured, which can result in a low cocoa content and poor quality. On the other hand, harvesting too late can cause the pods to rot or even cause the beans to germinate. It is essential for producers to recognize the signs of ripeness to ensure pods are harvested at their peak.

Determining the Ripeness of Cocoa Pods
The most common method for determining whether a pod is ripe is to observe the color of the shell and tap it. If the sound is hollow, this generally indicates that the pod is ripe and ready to be harvested. Experienced pickers can also assess the hardness of the shell and its texture to confirm that the harvest is due.
When is the Cocoa Pod Harvest?
The timing of cocoa pod harvesting varies depending on the region and climate. In some areas, cocoa pods ripen year-round, allowing for constant, continuous harvesting. This is often the case in countries near the equator, where the climate is favorable for cacao tree growth. However, in other regions, such as West Africa, harvesting is concentrated into two main periods: a first "main harvest" at the beginning of the year, and a second, smaller harvest in the middle of the year.
The harvesting periods are also influenced by the type of cacao tree being cultivated. Typically, cacao trees produce pods twice a year, but there are exceptions. In certain regions, specific climatic conditions such as dry or wet periods can affect the harvesting cycle.
It is essential for producers to closely monitor the development of the pods to avoid harvesting too early or too late. This delicate task requires careful observation and a deep understanding of each plantation’s rhythm.

How Are Cocoa Pods Harvested?
Harvesting cocoa pods is a manual task, carried out by experienced pickers with expertise in the field. These professionals use specific tools to pick the pods while preserving the integrity of the trees and future crops. s.
Manual Harvesting Process
The cocoa pods are harvested one by one. For easily accessible pods, pickers typically use a sharp knife or machete. For those higher up in the tree, pickers use a pole equipped with a sharp blade. This method allows them to cut the pods without risking damage to the tree. A clumsy cut could injure the tree, leaving it vulnerable to fungal infections or other diseases.

Why Is Hand Harvesting Important?
Manual harvesting of cocoa pods is a hallmark of quality for the cocoa beans. This process ensures that only ripe pods are picked. It is crucial that pickers are precise and delicate to avoid damaging the tree or the remaining fruit. Additionally, manual harvesting minimizes the risk of contamination of the beans by mold or microorganisms, which could spoil their quality.
Another advantage of manual harvesting is the preservation of the pods and their contents. The pods must be handled carefully to prevent damage to the beans inside. If a pod is opened too abruptly, it can lead to premature fermentation of the beans, which can alter their flavor and aroma.
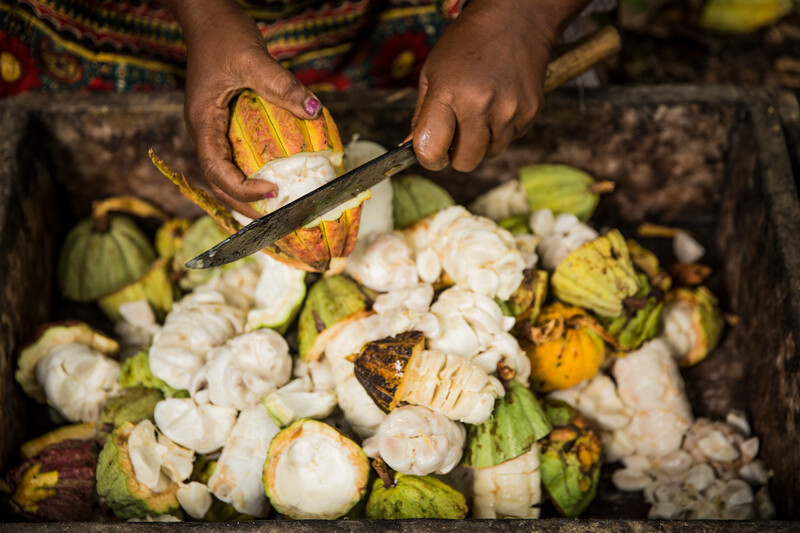
Cracking: A Crucial Step After Harvest
Once the cocoa pods are harvested, the next step is cracking, which involves opening the pods to extract the cocoa beans. The pods contain between 15 and 60 beans surrounded by a white, sticky pulp called mucilage. This pulp must be removed quickly, as the beans begin to ferment once exposed to air. Poor management of this stage can compromise the quality of the beans, as they risk being affected by fermentation or contamination.

Manual Cracking Method
Manual cracking is the most common and bean-friendly method. Using machetes, pickers gently open the pods to remove the beans. This method allows for careful control over the quality of the beans, removing damaged ones and preserving those that are healthy.
Mechanical Cracking: An Industrial Alternative
Although manual cracking is preferred for its gentleness, some companies use machines to speed up the process. These machines, which use blades or grinders, allow for the rapid processing of large quantities of pods. However, this method is not ideal for the quality of the beans. Machines can damage the cocoa beans, which can harm their flavor and texture. Additionally, the speed of mechanical cracking can lead to less controlled fermentation, further compromising the quality of the cocoa.
At Valrhona, manual cracking is preferred to ensure the best possible quality beans. The brand places particular emphasis on preserving the integrity of the beans, as this stage determines their flavor and aroma.

Valrhona’s Commitment: Towards Sustainable and Respectful Harvesting
At Valrhona, the commitment to sustainable and ethical cocoa production is at the heart of every step of the chocolate-making process. Manual harvesting and cracking are part of the practices that ensure high-quality cocoa while respecting the producers. The company seeks to work closely with cacao farmers to provide them with tools and training aimed at improving the quality of their crops while respecting agricultural traditions.
This commitment is further reinforced by partnerships with local producers to promote a fair, sustainable, and environmentally respectful cocoa supply chain. To learn more about Valrhona’s initiatives, feel free to visit the Cité du Chocolat Valrhona and explore the interactive journey that traces the history of chocolate-making.
Conclusion: Cocoa Pod Harvesting—A Key Factor in Exceptional Chocolate!
Cocoa pod harvesting and cracking are fundamental stages in the production of high-quality cocoa beans. Their execution must be meticulous and respectful of traditions to ensure exceptional chocolate. Managing each step, from manual harvesting to cracking, has a direct impact on the quality of the cocoa beans and, therefore, the final taste of the chocolate. At Valrhona, these practices are carefully followed to offer refined chocolate that meets the expectations of chocolate lovers and pastry professionals alike. Thanks to a strong commitment to sustainable and environmentally respectful production, the brand is pushing the boundaries in the cocoa industry.
If you want to learn more about the art of cocoa harvesting and discover the secrets of chocolate-making, don't hesitate to check out our other articles on the Cité du Chocolat Valrhona blog. You’ll find tips, tricks, and practical information about the world of chocolate and pastry. While in the region, you can also visit the Cité du Chocolat Valrhona to continue expanding your knowledge!